What is arthritis?
Arthritis, despite affecting 1 in 6 Australians, which totals nearly 4 million people, remains surprisingly misunderstood. While it’s common to think of arthritis as being something which only impacts the elderly, arthritis sufferers range all the way from babies through to the elderly. This misconception is likely due to the fact that arthritis is an umbrella term for over 100 different medical conditions. The things these conditions have in common is that they affect the musculoskeletal system, specifically the joint areas, where two or more bones meet. Arthritis works by damaging the joints, with this damage then typically resulting in pain and stiffness. Most forms of arthritis are thought to be auto-immune conditions. These are conditions where the body’s immune system attacks its own joint tissues. Common symptoms to look out for when it comes to arthritis include:
- Pain. This can vary from dull aches to shooting nerve pain.
- Stiffness or limited movement around joints.
- Swelling in specific joint areas.
- Redness or warmth in specific joint areas.
- The symptoms listed above can also be linked to more general symptoms like tiredness, weight loss and feeling unwell.
Due to the large variety of arthritis conditions it is incredibly important to identify your specific condition to ensure that selected treatments achieve an optimal effect. Be sure to consult your doctor as soon as possible if you have any of the symptoms previously mentioned, as early detection through examination of your joints can help to minimise damage. Early detection can be difficult though and the help of a rheumatologist, a doctor specialising in arthritis, may be beneficial.
The most common form of arthritis
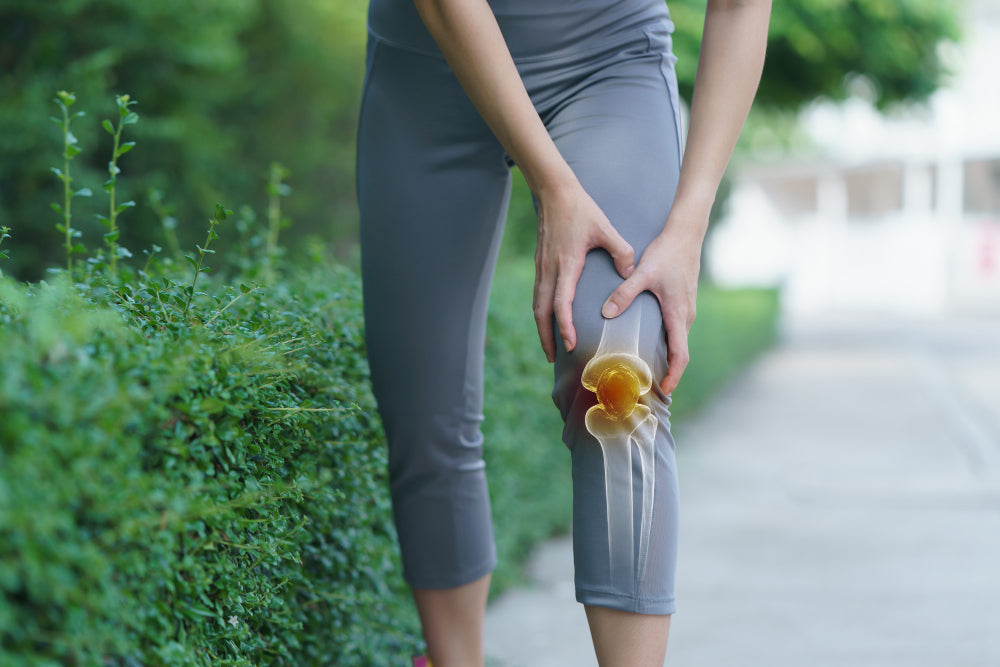
Osteoarthritis is far and away the most common form of arthritis. Despite the misconception that this is typically a result of wear and tear on a joint, it is caused by changes in the tissue, which results in a gradual breakdown of the joint. This breakdown is specifically the cartilage, the flexible connective tissue between the bone, which provides cushioning. If the cartilage wears down enough then the bones can even begin to rub against one another, hence the pain and stiffness. Osteoarthritis can affect any joints but most commonly impacts upon knees, hips, fingers and big toes.
Typical factors contributing to osteoarthritis are:
- Aging. This is likely due to cellular changes, resulting in a degrading of the joint tissue.
- Being overweight or obese. This is due to an increased load on the joints.
- History of injury or surgery on a joint. This can form quickly or over time.
- Overuse from repetitive movements. This can be via work or hobbies.
- Joints that form incorrectly.
- Family history. This is particularly common with arthritis of the hands.
Anyone can suffer from osteoarthritis but it is more common in the elderly, especially among menopausal women. If present in young people then it is usually a result of one of the following:
- A joint injury.
- Abnormal joint structure.
- A genetic defect in the joint cartilage.
Treatment for arthritis
There are currently no medications which can cure arthritis, however studies are ongoing. Exercise and weight loss are highly beneficial but the medications focus specifically on pain relief and lowering inflammation. These range from basic pain relief medication, which can be purchased over-the-counter from any discount pharmacy, through to injections or surgeries, such as:
Analgesics
General pain relievers, such as paracetamol, are a great starting point to treat arthritis pain as they can be purchased from any discount pharmacy. They may not be effective though and the side effects need to be considered, particularly if you are on any other medications or if you are intending to take it over a long period of time.
Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
These go beyond just pain relief to also offer anti-inflammatory properties, which are highly useful when it comes to arthritis. Examples of NSAIDs include aspirin, naproxen, ibuprofen and diclofenac. Further examples include COX-2 inhibitors, such as; celecoxib and meloxicam. Lower dose forms of these medications can be purchased over-the-counter from any discount pharmacy, whilst higher dosage options will require a doctor’s prescription.
NSAIDs come in a variety of forms to suit a variety of needs and preferences, such as; tablets, capsules, creams, liquids, injections, sprays and suppositories.
It is highly important to be aware of the side effects of NSAIDS. All medications have side effects and NSAIDS are no different. They can range from mild symptoms like nausea, heartburn and indigestion, right through to less common but highly serious side effects like stomach bleeding or kidney problems. If suffering any heart related illnesses be cautious when buying over-the-counter from a discount pharmacy as over-the-counter NSAIDS have been linked to a small increase in the risk of a stroke or heart attack.
As a long term treatment these can be further problematic as the risk of side effects goes up if used regularly and for a long period of time.
The following factors increase the risk of side effects from NSAIDs:
- Having pre-existing medical conditions relating to the stomach, heart, pancreas, kidney or liver.
- Being older than 65, especially if frail, as NSAIDs increase the risk of strokes.
- Are pregnant or planning a pregnancy.
- Are dehydrated. This is particularly dangerous for the youth and the elderly.
- Are already taking medications which contain NSAIDs.
- Drink alcohol.
- Take more than the recommended dose or continue to take it for an extended period.
Injections
Injections can be highly effective in treating the pain associated with arthritis. The two main types of injections are:
Beyond these two forms of injections the effectiveness of other options becomes very unclear, with most choices not recommended by professionals.
With well targeted treatment, arthritis can be managed effectively and does not need to ruin your quality of life.